If you’re a nursing student who intends on gaining some in-depth knowledge of the VEAL CHOP nursing method, then you’ve definitely come to the right place. This blog will walk you through everything you will need to know about this particular method in nursing. So without further ado, let’s begin!
At first, let’s break down these terms and see what they actually mean. The “VEAL” stands for variable deceleration, early deceleration, accelerations, and late decelerations. This term aligns with “CHOP”, which is an acronym for cord compression, head compression, oxygenated or OK, and placental insufficiency.
This nursing mnemonic can help nursing students to remember the main concepts related to the monitoring of fetal heart rate. By familiarizing themselves with the mnemonic, they can quickly recognize the different patterns associated with common complications of pregnancy.
Components of VEAL CHOP
In this section, we will be analyzing every component of the VEAL CHOP nursing mnemonic. We will explain the meaning of each of the letters in the acronym and review clinical conditions that might affect the tracings of fetal heart rate.
V: Variable Decelerations
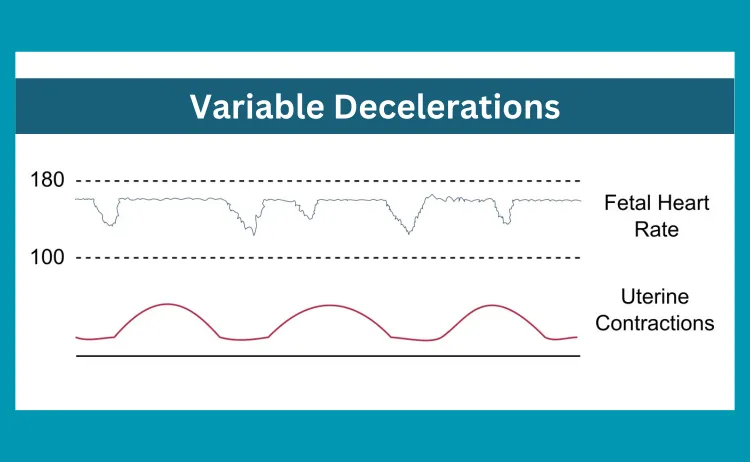
Variable deceleration is a fetal heart rate pattern that occurs in late pregnancy or early labor when the blood supply to the fetus decreases. The variable deceleration pattern indicates fetal circulation difficulties and can be a sign of serious complications, such as fetal distress or placental insufficiency. Variable decelerations are often benign, but recurrent decelerations can be alarming and may require immediate attention.
Causes
The causes of variable decelerations range from the mother and fetus’s positioning to true knot in the umbilical cord, nuchal cord entanglements, and insufficient amniotic fluid. To manage variable decelerations, it is important to adjust the mother’s position to alleviate umbilical cord compression. Head compression can also cause fetal heart rate decelerations during labor.
E: Early Decelerations
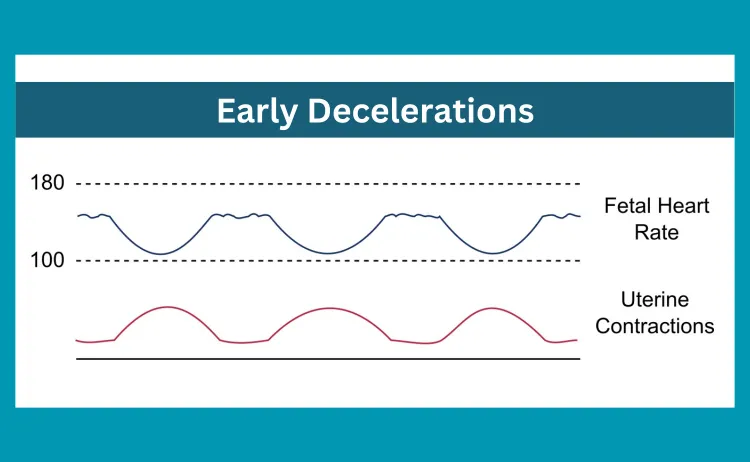
An early deceleration in VEAL CHOP (uterine contraction heart rate late deceleration) is a heart rate decrease in the fetus that follows the uterine contraction. It is typically observed during late decelerations of the fetal heart rate and is associated with uterine contraction. In general, early decelerations of the fetal heart rate are considered as a sign of head compression. The early deceleration of the heart rate indicates that the fetus is quickly reacting to changes in the environment.
The early deceleration also indicates that fetal head is being compressed. Thus, early decelerations need no emergent interventions as they are part of normal fetal heart rate patterns.
Causes
Early decelerations are a common concern during pregnancy, as they can indicate fetal distress. They may be caused by compression of the fetal head by the uterus or fetal heart rate deceleration due to decreased blood flow to the fetus.
A variety of interventions may help reduce early decelerations and provide comfort for the mother and fetus. These include: increasing the flow of oxygen to the fetus by changing the mother’s position during labor; administering oxygen; administering insulin; reducing uterine contraction strength; administering oxytocin; using fetal heart rate monitoring to detect early decelerations; and using postpartum fetal heart rate monitoring to detect early decelerations and ensure that adequate care is provided to the fetus following birth.
A: Accelerations
Accelerations in VEAL CHOP signify a change in fetal heart rate of more than 15 beats per minute above baseline that starts and peaks within 30 seconds. They’re seen as an increase in fetal heart rate of at least 15 beats per minute above baseline that starts and peaks within 30 seconds. These are common fetal heart rate patterns and are typically associated with any direct or indirect fetal movement.
Accelerations are used as an indicator of fetal well-being and normal acid-base balance. They are often used as a measure of fetal well-being. They’re associated with fetal movement, uterine contractions, vaginal examinations, applying pressure to the fundus, and the placement of internal monitoring instruments.
L: Late Accelerations
Late accelerations occur when the fetal heart rate (FHR) gradually decreases and returns to baseline during contraction. This nadir point can be seen after the peak contraction. These late accelerations may indicate fetal distress and require nursing attention to ensure fetal well-being.
Causes
In late pregnancy, the fetus undergoes a range of changes that can affect its growth and development. These changes may lead to fetal distress or complications during labor and delivery.
One common late-pregnancy complication is acceleration of the fetal heart rate (FHR). This may occur in cases where the fetus’s oxygen supply is restricted and heart rate deceleration occurs as a result. To manage late decelerations, it is important to identify the cause and treat it. In some cases, treatments such as fetal heart rate monitoring, intravenous oxygen, or medications may be required. During labor, fetal heart rate must be monitored closely and interventions should be initiated immediately if any deceleration occurs. Additionally, rapid umbilical cord compression or placental abruption may require immediate action to save the fetus’s life.
C: Cord Compression
The “C” in CHOP stands for cord compression, which is the cause of variable decelerations. These are caused by the umbilical cord’s impermanent compression or chemoreceptor response to hypoxia.
H: Head Compression
The “H” represents head compression, the cause of early deceleration. Due to high intracranial pressure, a non-hypoxic reflex may lead to early decelerations.
O: Okay!
In the VEAL CHOP nursing mnemonic, “O” stands for “okay!”. Accelerations are usually caused by scalp stimulation, fetal movement, or contractions. On the fetal monitor, accelerations are common and reassuring pattern.
P: Placental Insufficiency
Lastly, the “P” represents placental insufficiency, which causes late decelerations. This may be due to excessive uterine activity, insufficient uterine perfusion, fetal hypoxia and maternal hypotension.
VEAL CHOP Interventions
VEAL CHOP is used to remember the nursing interventions for fetal heart rate monitoring. This includes the nursing steps of evaluating, assessing, listening, and asking.
Visualize: Use your nursing assessment skills to identify what’s happening with the fetus’ heart rate. This may include making a fetal heart rate chart or drawing a heart on the fetal monitor.
Evaluate: This may include checking for signs of distress such as pale skin, limpness, or not breathing normally. It also includes checking for conditions known to affect fetal heart rate such as hypothermia or shock.
Assess: In this step, you need to determine how the fetus is responding to treatment. This step includes using the ScvO2 or pulse oximeter to assess oxygenation and/or heart rate patterns, watching the fetal heart rate on the monitor, or palpating abdomen and heart rate.
Listen: You must also put your nursing assessment skills to test in order to listen for signs of distress in the fetus such as increased heart rate, agitation, compression caused by fluid in the uterus, or decreased movement on the fetal heart rate monitor.
Count: Here, you must be able to count fetal heartbeats naturally when they occur. This is an important part of assessing fetal heart rate and can help you determine when a contraction has ended and another one is beginning.
Conclusion on Veal Chop Nursing
In the world of healthcare, ensuring the safe delivery of babies is paramount. That’s where VEAL CHOP Nursing comes in. This is a tool used by healthcare professionals to monitor fetal heart rate patterns during labor and delivery.
By using this acronym, nurses can quickly spot potential problems and take the necessary steps to ensure the safe delivery.
In order to provide the best possible care for both mother and child, it is important that nurses are properly trained and educated in the care of calf chops. These clear and concise guidelines can help reduce the risk of adverse fetal harm and improve overall maternal and neonatal health.
Read more: How to Become a Neonatal Nurse?
FAQs
What does the VEAL CHOP mean in nursing?
In nursing, the VEAL CHOP is a mnemonic that serves as a tool for nurses in determining the causes of change in fetal heart during labor.
What is the VEAL CHOP fetal heart rate?
It is used to establish the fetal heart rate during contractions in labor.
What are the interventions for the VEAL CHOP?
If variable or late decelerations occur, this means that there is absence of good oxygenation in the fetus and the patient must be turned to her side and given oxygen. In the case of early decelerations or accelerations, no emergent interventions are required.
What is being actually assessed through the VEAL CHOP method?
Through this method, the fetal heart rate (FHR) during labor contractions is assessed.

Leave a Reply